Despite being mentioned as the mainstream power source in the future, renewable energy still has weaknesses in terms of stability and ability to ensure the safety of the power transmission system. In Vietnam and many countries around the world, that fact is posing an urgent requirement to rapidly develop methods to solve the problem of energy storage in order to make the most of natural resources.
Risk of system overload
The period of 2019 - 2020 witnessed the hot growth of renewable energy, especially solar power due to the "catalyst" from the preferential mechanism of FIT prices. By the end of 2021, the total capacity of renewable energy sources in Vietnam will reach 20,670 MW, accounting for 27% of the country's power source.
Despite the rapid growth rate, there is an undeniable fact that renewable energy projects are showing many limitations. The reason is that renewable energy depends almost entirely on nature, so the operating conditions of power plants are unstable due to cloudy days and calm winds.
In addition, the time when solar and wind farms reach their maximum capacity is always different from when the load demand is high. Specifically, when the solar radiation is highest at around 10am - 2pm, the demand for electricity is low; But by the evening time (17:30-18:30), the demand for electricity is high, and solar power is very low.
Example of electricity load chart on December 30, 2020 (source: EVN)
Therefore, many solar power projects so far have not been connected to the national grid because of concerns about overloading the power transmission grid, causing unsafety to the power regulation system. Even many projects have to operate in a state of reduced capacity compared to design, causing great waste for investors.
According to the Draft Power Plan 8, by 2030, the total capacity of wind power and solar power can reach a maximum of 37,107 MW with the best power output of about 33,087 kWh (22.7% of the country's electricity). In the vision to 2045, the Draft Master Plan also expects that the above indicators will increase by 5-6 times. The urgent problem at the moment is to build a commensurate electricity storage system to make the most of natural resources and accelerate the carbon neutralization process as committed by Vietnam.
The inevitable development trend
Around the world, the need to store energy from renewable energy has appeared for a long time. According to the experience of many countries, when the penetration of renewable energy into the electricity system reaches at least 15% of the national electricity scale, the investment in the energy storage system (ESS - Energy Storage System) ) would make a lot of sense.
According to data from Global Market Insight, investment in ESS exceeded $340 billion in 2018. It is forecast that the compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of this sector will maintain around 6.9% to the size of the market. This market will reach 500 billion USD by 2025. Large-scale energy storage technologies will mainly be hydroelectricity and chemical batteries.
Simulation of a typical pumped-storage hydroelectric plant model (source: ecogeneration)
The Asia-Pacific region will see investment growth for ESS of 23.5% during 2020-2025. In particular, the Chinese and Japanese markets alone will account for more than 75% of the entire region.
In Europe, between 2014 and 2020, the Horizon fund, which funds research projects and initiatives by the European Commission, invested US$6.57 billion to improve the efficiency of clean energy technologies. , including tidal power, ESS system and grid. In the UK, the government recently approved spending £68 million on two projects to produce and store hydrogen energy and store it by gravity.
For the United States, the CAGR of investment in the ESS system in the period 2018-2024 will maintain 33% per year, increasing the market size from $400 million to $4 billion within 7 years. In 2018, the world's largest energy storage plant went into operation in California, using chemical battery technology that is very popular in this country. According to estimates by the Energy Storage Association of America, it is estimated that the country needs 100GW of stored energy by 2030 to meet its climate commitments.
The world's largest Gateway energy storage plant with a scale of 250MW, located in San Diego County, California, USA
Development prospects in Vietnam
Around the world, energy storage systems are classified according to three levels of scale, including large storage systems, small storage systems and micro storage systems.
Large storage system includes: stored hydroelectricity; storage by air compression; gas storage; seasonal and inter-seasonal storage. Small storage systems using BESS (Battery Energy Storage System) technology with sizes from 1 MW to 500 MW, usually applied to transmission grids, distribution grids, or renewable energy power plants. Micro-storage systems ranging in size from a few tens to several hundred kW are intended for households, distribution grids, and moving equipment.
In Vietnam, the draft Power Plan 8 sets a target that by 2030 the electricity storage capacity of the system will reach 2400MW with stored hydroelectricity. By 2045, the total cumulative storage and storage capacity will increase to 28,950 MW nationwide.
Construction of the discharge tunnel section 3 of Bac Ai hydropower plant
According to the plan, by 2030, Vietnam will have 2 storage hydroelectric plants with a total capacity of 2400MW, namely Bac Ai and Phuoc Hoa hydropower plants, both located in Ninh Thuan province. These two projects are expected to have a lifespan of up to 40 years, play an important role in helping to reduce line overload, increase the absorption of renewable energy sources, and reasonably adjust the load chart to support other power plants to operate more efficiently.
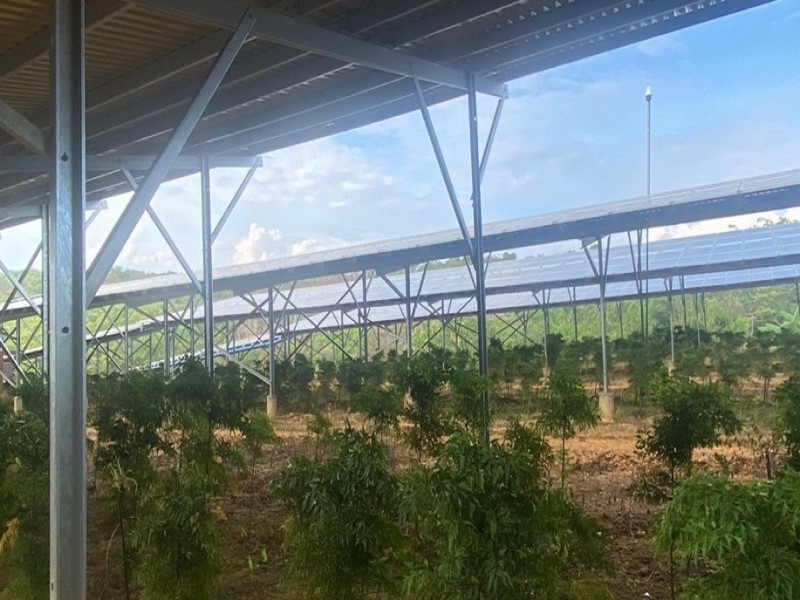
In addition to the above model, the BESS energy storage battery solution is also starting to be piloted to evaluate its applicability and create a basis for building a legal framework for this field. Specifically, in 2021, the US Consulate General in Ho Chi Minh City sponsored US$2.96 million for AMI AC Renewables Company to implement a pilot project to develop BESS in Vietnam. It is expected that the battery system will be connected to the company's 50MW solar power plant in Khanh Hoa province.
AMI AC Renewables solar power plant in Cam Lam district, Khanh Hoa province will be the first locality to pilot building an energy storage system in Vietnam.
Thus, it can be seen that the energy storage system will be the next investment trend that cannot be different in any country developing renewable energy, not only Vietnam. The investment right now will create the necessary premise to ensure stable operation of the power grid system and improve the efficiency of renewable energy projects./ .