With the advantages of nature; many preferential policies and mechanisms; Along with ambitious commitments on carbon neutrality at COP 26, Vietnam has many conditions to attract foreign investment in the field of green energy.
Diversified development potential
In Vietnam, solar power and wind power are two forms of energy with the most potential for development.
With its geographical location near the equator, Vietnam has up to 2000-2600 hours of sunshine per year, most distributed in the southern provinces; The average annual total solar radiation is about 230-250 kcal/cm2/day.
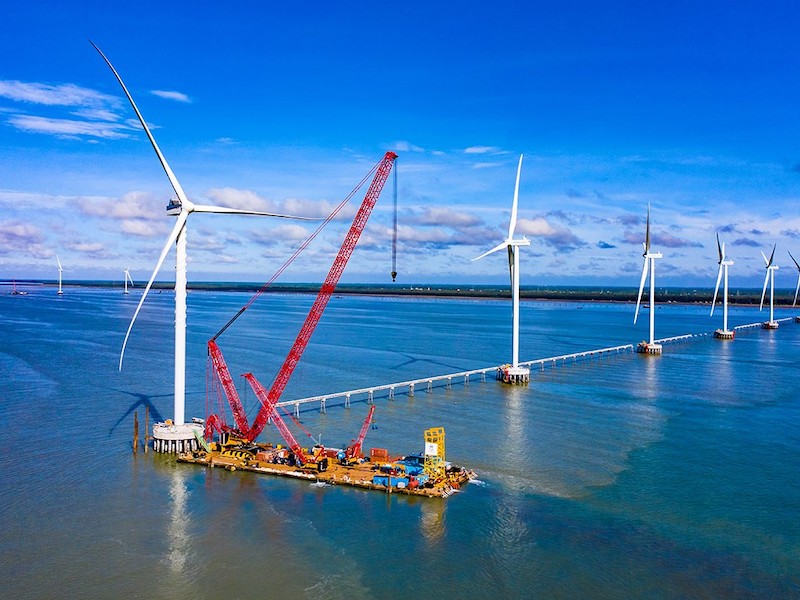
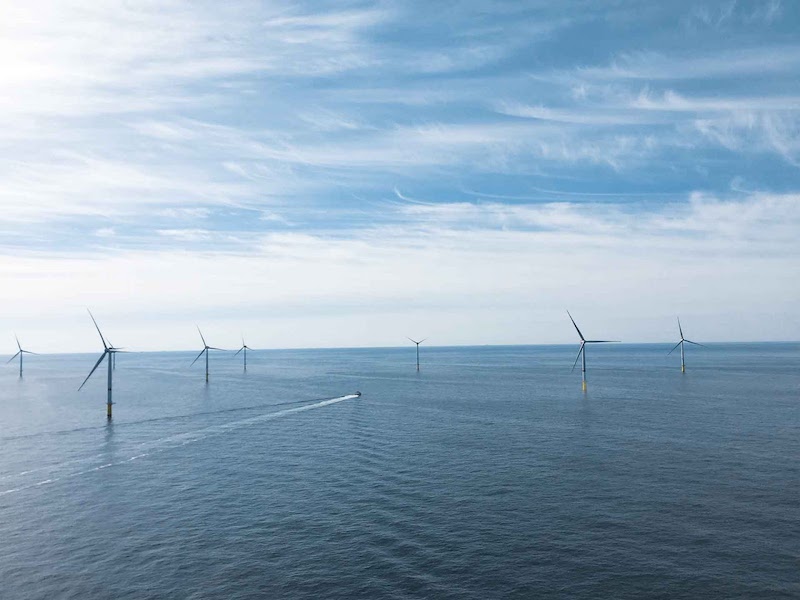
With wind power, a World Bank study in 2019 showed that 39% of Vietnam's area has an average wind speed of over 6m/s at an altitude of 65m, the potential capacity from this source can reach 512GW. Vietnam's 200m deep sea can produce 475GW of offshore wind power. In which, the southern sea area is 142,000 km2 wide and has good development conditions with wind speed of 7-10m/s at a depth of 100m.
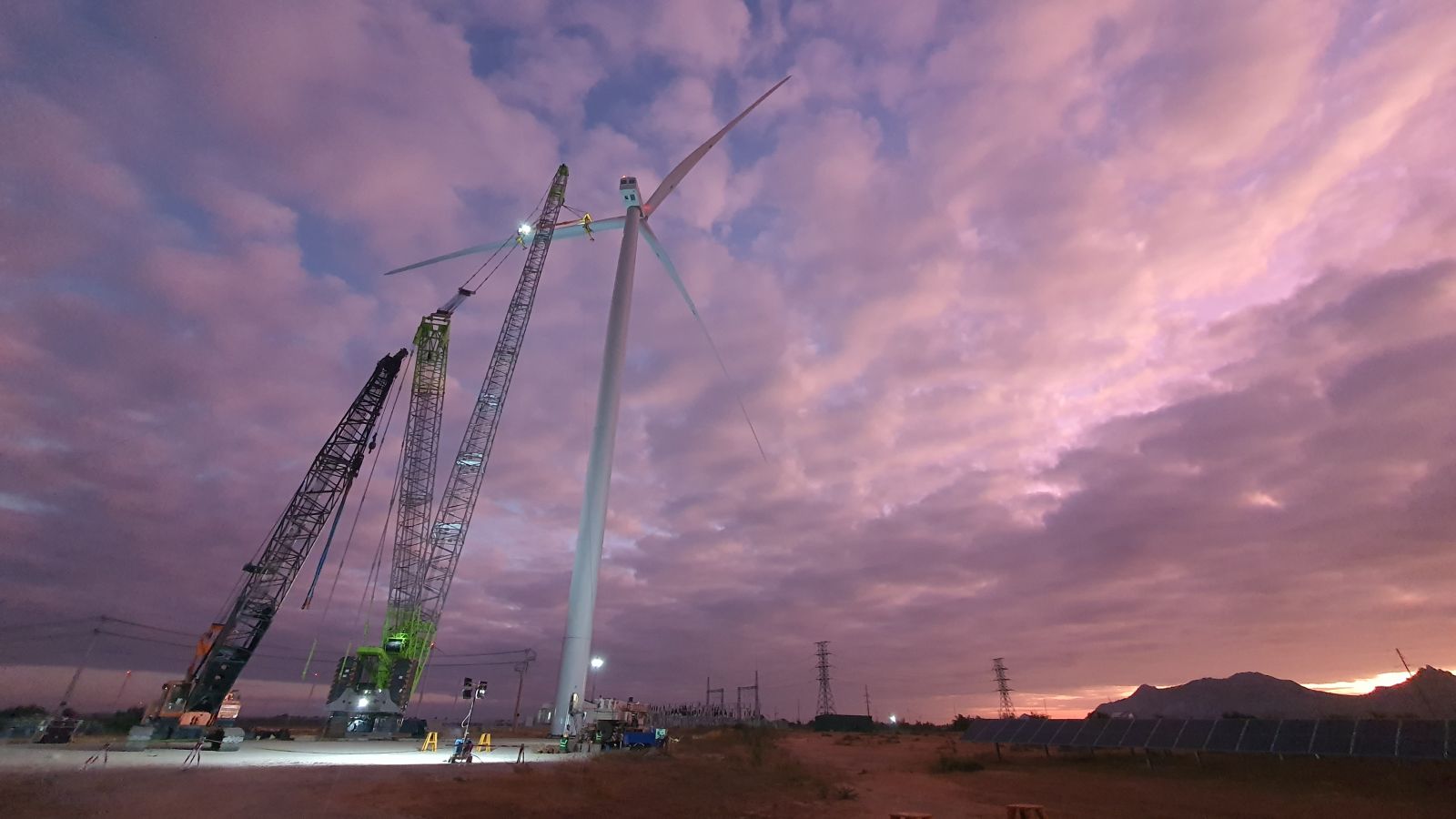

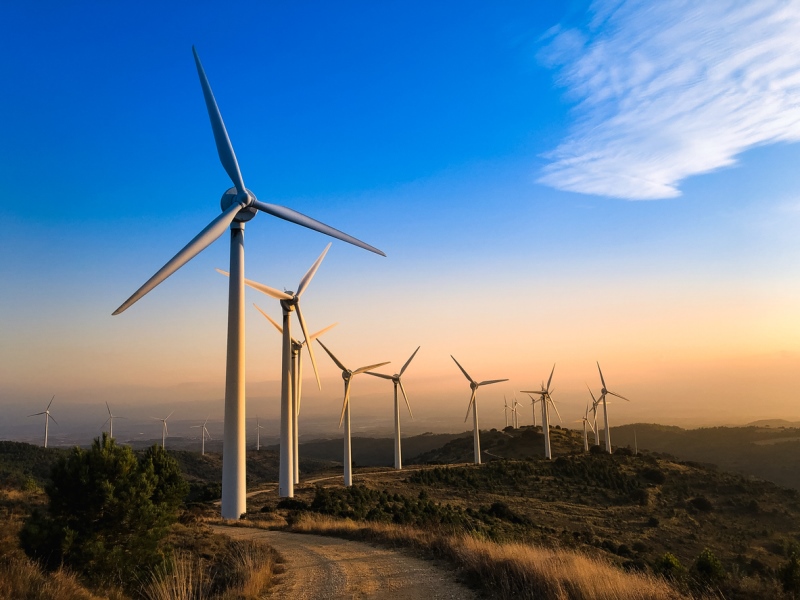
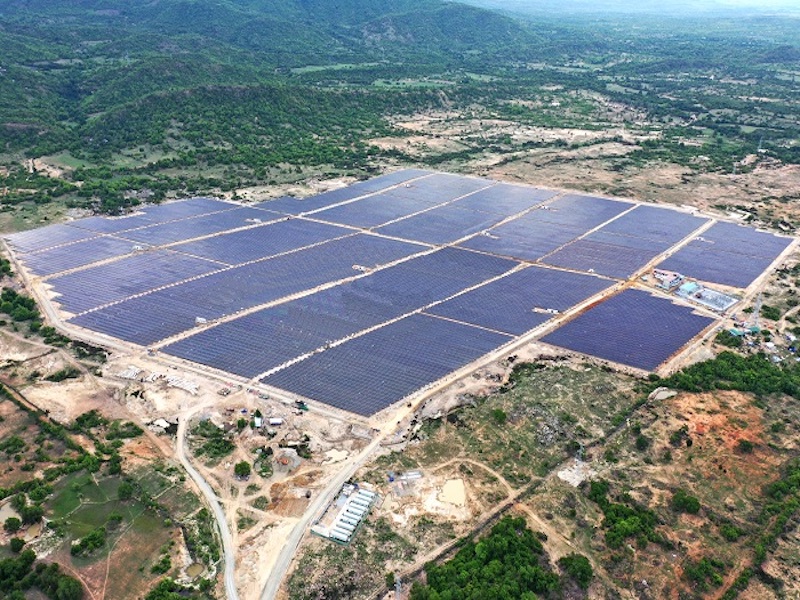
A solar power project combining wind power of RT Energy in Ninh Thuan
Vietnam is also evaluated by experts as a country with great potential for biomass energy from the development of agro-forestry activities and the expanding urbanization process. Common biomass sources in Vietnam include wood and firewood; by-products of forestry, cultivation and animal husbandry; domestic solid waste. Currently, the country has an average biomass of 160 million tons/year each year. According to Power Construction Joint Stock Company 3, it is estimated that by 2030 and 2050, the total potential of biomass energy will reach 113 million MWh and 120 million MWh, respectively. By 2030, biomass energy across the country will increase by about 1.9%/year.
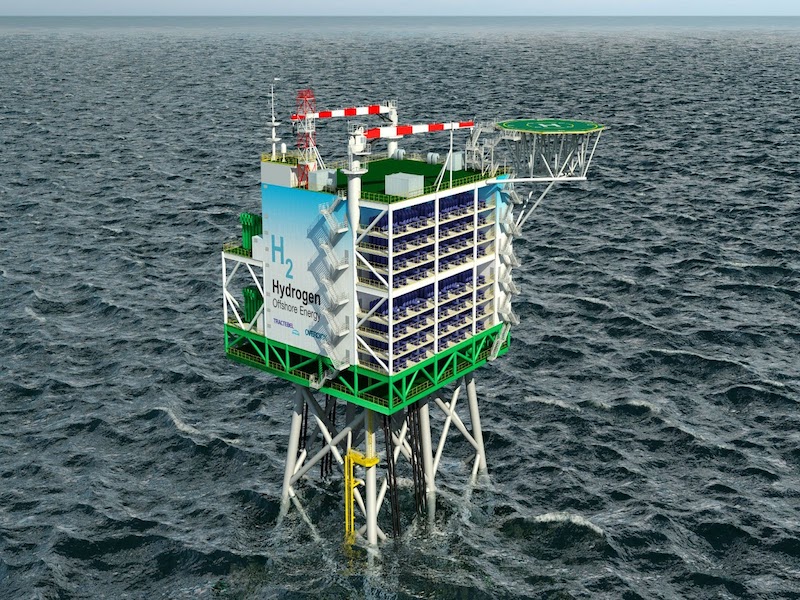
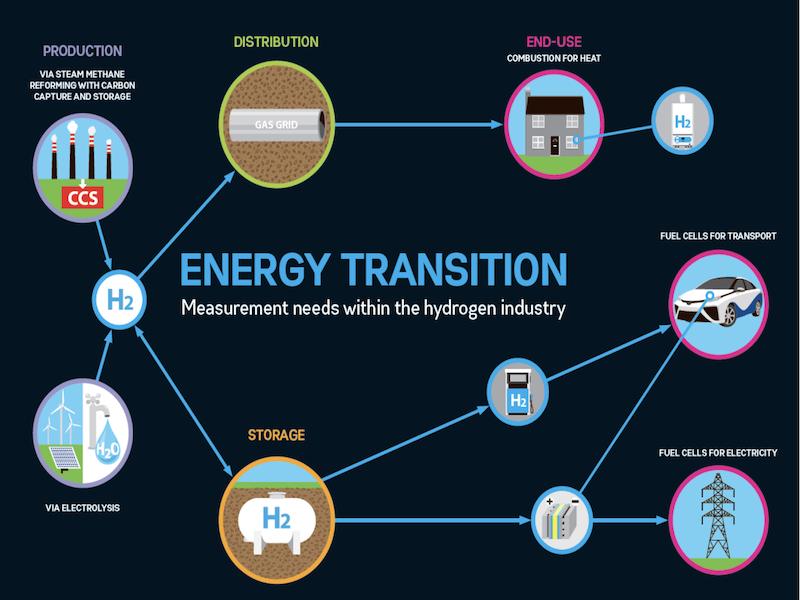
In addition to the above-mentioned energies, in the development strategy, Vietnam also aims to research, develop and pilot the use of many new forms of energy such as geothermal, tidal power and most notably the production model. Green hydrogen tied to offshore wind power.
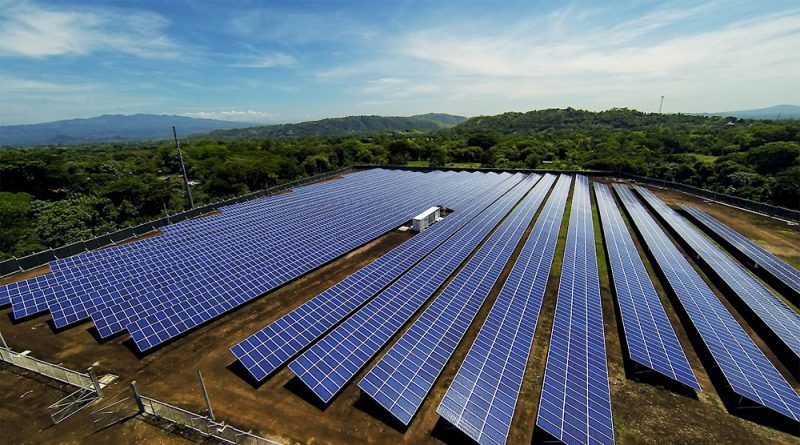

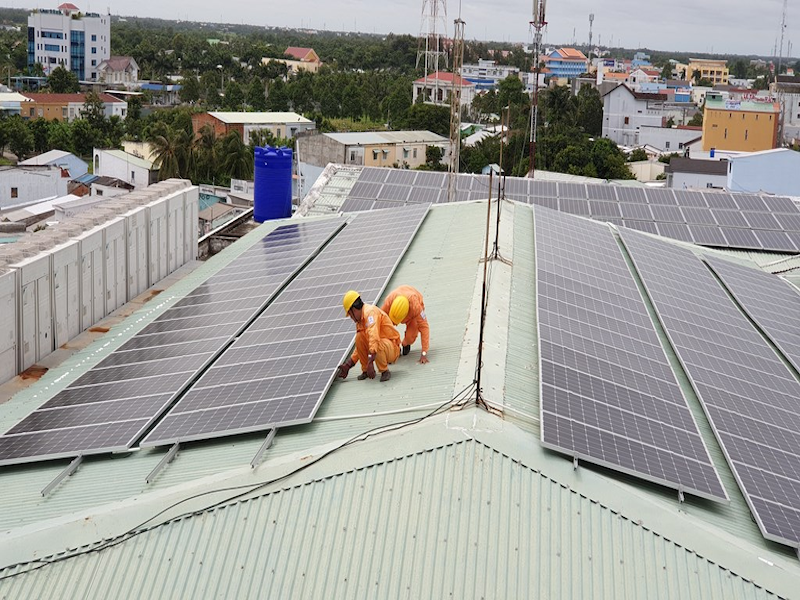
In the period of 2019-2020, up to 16.5GW of solar power has been installed, equivalent to 23.9% of the total capacity of the country.
Taking advantage of these conditions, the total capacity of renewable energy sources in Vietnam in 2021 has reached 20,670 MW, an increase of 3,420 MW compared to the previous year and accounting for 27% of the country's electricity supply.
Ambitious goals and preferential policies
At COP 26, Vietnam made a strong commitment to be carbon neutral by 2050. In order to fulfill the set target and take full advantage of the advantages of nature, the Draft Power Master Plan 8 has been drafted. outlines the development roadmap of Vietnam's renewable energy, along with a series of policies to attract both domestic and foreign investment in this field.
According to Power Planning 8, by the middle of this century, Vietnam aims to have about 129,851-201,647MW of electricity from renewable energy, which is 6.3-8.7 times higher than the draft target set for 2025.
With the energy conversion management plan, Vietnam needs to spend 16.6 billion USD each year to invest in electricity development. In the current context, the construction cost of key projects with large capacity, power transmission and storage systems is the top concern of renewable energy development. In addition, to offset the costs incurred when implementing the scenario of zero emissions by 2050 at COP 26, Vietnam needs $19 billion to keep electricity prices at normal.

In the field of electricity, infrastructure is always the item that requires the most investment capital
To solve the above problem, the Government of Vietnam has issued many mechanisms on taxes, fees and land use to attract investment capital from foreign investors.
Enterprises investing in renewable energy in Vietnam will be exempt from corporate income tax for 4 years from the year of taxable income. Over the next 11 years, the tax rate will gradually increase from 5% to 10%; Since then, this number has remained at 20%. Projects that develop and use renewable energy sources are also exempt from import tax on goods imported to create fixed assets for the project. The environmental protection tax in this case is also 0%.
In the province where the project is located, the land rent will also be reduced according to the regulations of that locality. The Vietnam Development Bank (VDB) also accompanies businesses with loans up to 70% of total investment costs with an interest rate equivalent to that of 5-year government bonds plus 1%/ five.
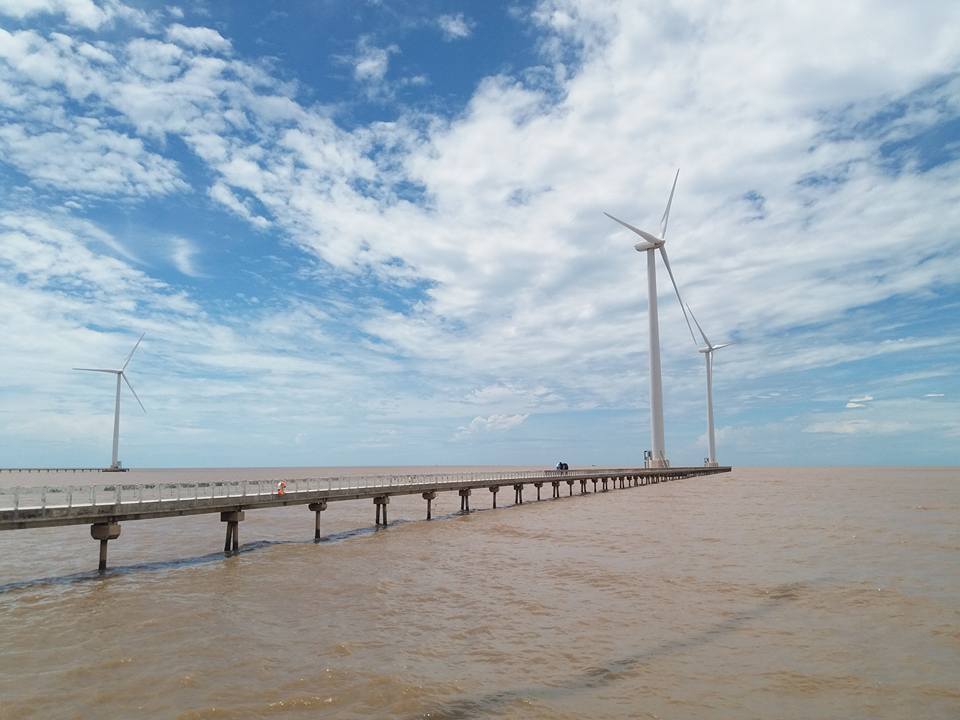

Bac Lieu wind power plant is the first wind power plant in Vietnam. The project's turbines are all provided by General Electrics (USA).
Proof of the attractiveness of open policies is the increase in the number and size of FDI projects investing in renewable energy. According to data from the Foreign Investment Agency (Ministry of Planning and Investment), in 2009, there were only 2 investment projects in the energy sector, worth $90.5 million. By 2021, the electricity production and distribution industry has attracted a total foreign direct investment of more than 5.5 billion USD, accounting for nearly 25% of the total registered FDI in Vietnam in the first 9 months of the year.
In the vision to 2050 in Vietnam, renewable energy will gradually replace traditional power generation sources and play a decisive role in the national economy. Thus, choosing clean energy sources is the main trend of Vietnam in the coming period. With abundant development space and open investment mechanism, the opportunities of foreign enterprises in this market will certainly be very open./.